In the realm of global agriculture trade, Indonesia has steadily emerged as a powerhouse, particularly in the cocoa sector. This exponential surge in Indonesia’s cocoa exports is not only reshaping the country’s economic landscape but also positioning it as a pivotal player in the global cocoa market. This transition is a testament to Indonesia’s strategic cultivation, innovative processing techniques, and robust trade policies that are collectively fostering a thriving cocoa industry. This article delves deep into the facets of this ascent, exploring how Indonesia’s cocoa exports are experiencing a significant surge and the implications thereof.
Introduction to Indonesia’s Cocoa Industry
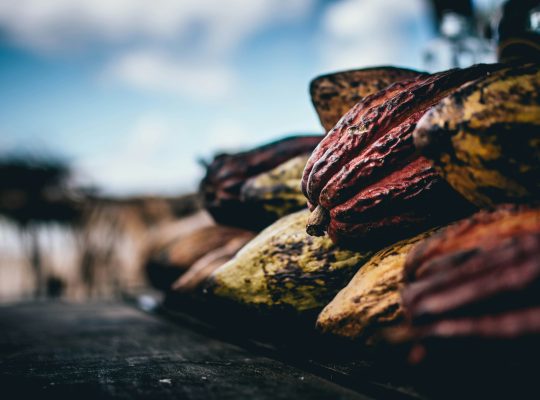
Nestled within the rich, tropical biodiversity of Indonesia, cocoa finds an ideal habitat for growth. Spanning regions like Sulawesi, Sumatra, and Java, Indonesia’s cocoa plantations are a vital component of its agricultural fabric. Historically recognized as one of the world’s top cocoa producers, the country’s journey from a modest cocoa cultivation landscape to becoming a significant exporter is a narrative of strategic agricultural evolution and economic foresight.
Factors Fueling the Surge in Exports
Quality Enhancement and Cultivation Innovations
Recent years have seen Indonesia make substantial strides in enhancing the quality of its cocoa beans, a pivotal factor driving the surge in exports. Through the adoption of advanced cultivation techniques and investment in research and development, Indonesia has improved both the quality and quantity of its cocoa yield. These innovations encompass better plant stocks, effective pest management practices, and adoption of sustainable farming methods that not only increase yield but also ensure better quality cocoa beans.
Strategic Government Policies
The Indonesian government has played a crucial role in this ascent, introducing favorable policies and incentives aimed at boosting the cocoa sector. These policies include subsidies for cocoa farmers, support for cocoa sustainability programs, and trade agreements that enhance access to international markets. Furthermore, the government actively collaborates with local and international agencies to provide training and resources to cocoa farmers, aiming to upscale their production capabilities and quality.
Expanding Global Demand for Cocoa
The global demand for cocoa products, particularly in emerging markets, has witnessed a notable upswing. With the growing popularity of chocolate and cocoa-based products, Indonesia’s strategic move to capitalize on this demand has been timely. The country’s ability to cater to both the bulk market and the premium segment, where there’s a growing appetite for sustainably produced cocoa, has significantly contributed to the surge in exports.
Infrastructure and Logistical Advancements
Investments in infrastructure and logistics have been pivotal in supporting Indonesia’s cocoa export surge. Enhanced port facilities, better storage capabilities, and efficient logistics services have streamlined the export process, reducing bottlenecks and ensuring timely delivery of cocoa beans to international markets. These improvements have also made it viable for Indonesia to export cocoa not just as raw beans but also as semi-processed and processed products, adding value along the supply chain.
Implications of the Surge
Economic Impact
The surge in cocoa exports has had a profound impact on Indonesia’s economy, contributing significantly to the agricultural sector’s GDP. It has fostered economic growth in cocoa-producing regions, creating employment opportunities and improving the livelihoods of farmers and communities involved in cocoa cultivation and processing.
Environmental and Social Considerations
While the surge in cocoa exports presents numerous opportunities, it also poses environmental and social challenges. The expansion of cocoa plantations has raised concerns over deforestation and the conversion of high-conservation-value lands into agricultural use. To address these challenges, Indonesia is gradually embracing sustainable cocoa farming practices, entailing certifications like Rainforest Alliance and UTZ, which promote environmental sustainability and social responsibility.
The Road to Sustainability
The global market’s increasing insistence on sustainability has impelled Indonesian cocoa exporters to adopt sustainable practices. Initiatives aimed at improving the environmental footprint of cocoa cultivation, enhancing biodiversity, and ensuring fair trade practices are gradually taking center stage. These efforts not only contribute to environmental conservation but also enhance the global competitiveness of Indonesia’s cocoa industry.
The Future Outlook
Looking ahead, the trajectory of Indonesia’s cocoa exports appears promising. With the global chocolate market projected to grow, the demand for high-quality, sustainably produced cocoa is set to rise. Indonesia, with its strategic initiatives and commitment to sustainability, is well-positioned to meet this demand. However, the challenge lies in balancing economic growth with environmental stewardship and social responsibility—a challenge that Indonesia is gearing up to address head-on.
Conclusion
Indonesia’s surge in cocoa exports is a multifaceted achievement, underpinned by quality enhancement, strategic policies, global market alignment, and infrastructural development. As Indonesia continues to navigate the complexities of global trade and sustainability, its cocoa industry stands as a beacon of potential and progress. Embracing sustainability, improving farmers’ welfare, and leveraging technological advancements remain pivotal for Indonesia’s cocoa sector to thrive in the global arena, ensuring that the sweetness of its cocoa beans is matched by the sustainability of its cultivation and export practices. Through concerted efforts and strategic direction, Indonesia’s cocoa industry is set to continue its impressive journey, contributing not just to the global cocoa market but also to the sustainable development of the nation.